使用原型实例指定要创建对象的类型,通过复制这个原型来创建新对象。
Class Diagram
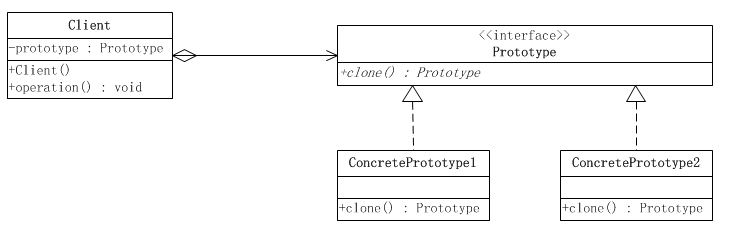
Implementation
原型接口
1
2
3
4
5
| public interface Prototype {
Prototype clone();
String getName();
void setName(String name);
}
|
原型实例
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
| public class ConcretePrototype1 implements Prototype {
private String name;
public Prototype clone() {
ConcretePrototype1 prototype = new ConcretePrototype1();
prototype.setName(this.name);
return prototype;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Now , This Prototype is ConcretePrototype1 , name = "+this.name;
}
}
public class ConcretePrototype2 implements Prototype {
private String name;
public Prototype clone() {
ConcretePrototype2 prototype = new ConcretePrototype2();
prototype.setName(this.name);
return prototype;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Now , This Prototype is ConcretePrototype2 , name = "+this.name;
}
}
|
原型管理器(原型过多时使用)
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| public class PrototypeManager {
private static Hashtable<String,Prototype> map = new Hashtable<String, Prototype>();
public static void loadPrototype(){
ConcretePrototype1 prototype1 = new ConcretePrototype1();
prototype1.setName("prototype1");
map.put(prototype1.getName(),prototype1);
ConcretePrototype2 prototype2 = new ConcretePrototype2();
prototype2.setName("prototype2");
map.put(prototype2.getName(),prototype2);
}
public static Prototype getPrototype(String prototypeId){
Prototype prototype = map.get(prototypeId);
return prototype.clone();
}
}
|
测试类
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| public class PrototypeTest {
@Test
public void test() throws Exception{
PrototypeManager.loadPrototype();
Prototype p1 = PrototypeManager.getPrototype("prototype1");
System.out.println(p1);
Prototype p2 = PrototypeManager.getPrototype("prototype2");
System.out.println(p2);
}
}
|
Usage
- 对象之间相同或者相似,只有少部分属性不同
- 创建对象较为麻烦,复制对象较为简单时
Example
Refence
